High Voltage Ceramic Capacitor/ Super High Voltage Ceramic Capacitor
1KV

2KV

3KV

6KV

10KV

15KV

20KV

25KV

30KV
|
Specification Reference Standard |
GB/T 2693-2001 ; GB/T 5966-1996 |
|
Rated Voltage(UR) |
500 / 1K / 2K / 3K / 4K / 5K / 6K / 7K / 8K / 9K / 10K / 15K / 20K / 25K / 30K / 40K /50K VDC |
|
Capacitance Range |
1pF to 100000pF |
|
Voltage Proof |
<500V,2.5UR ; ≥500V≤3KV,1.5UR+500V ; >3KV,1.2UR |
|
Capacitance Tolerance |
NPO±0.5pF(D)±5%(J) ; SL±5%(J)±10%(K),Y5P,Y5U±10%(K ) ; Y5U,Y5V±20%(M) |
|
Dissipation Factor (tgδ) |
C<30pF,Q≥400+20C ; C≥30pF,Q≥1000 ,Y5P,Y5U,Y5V:tgδ≤2.0% ; Y5P(Low loss type):tgδ≤0.5% ; Y5R:tgδ≤0.3% |
|
Insulation Resistance(IR) |
IR≥10000MΩ,1min,100VDC,IR≥4000MΩ,1min,100VDC |
|
Operating Temperature |
-25℃ to +85℃ |
|
Temperature Characteristic |
NPO,SL,Y5P,Y5U,Y5V |
|
Flame Retardant Epoxy |
UL94-V0 |

Application Scenario

Charger

LED lights

Kettle

Rice cooker

Induction cooker

Power supply

Sweeper

Washing machine
Applied in Various Fields.
Widely used in various electronic circuits and electronic complete machines, high and low voltage power supplies, controllers, industrial power supplies, motor filters, electronic ballasts, communication equipment, energy sources, computers and peripheral products, audio equipment, small home appliances, air conditioners , medical equipment, security and lighting and other consumer electronic products.


Certifications

Certification
We have passed ISO9001 and ISO14001 management certification. We manufacture products based on the GB standards and IEC standards. Our safety capacitors and varistors have passed CQC, VDE, CUL, KC, ENEC, CB and other authoritative certifications. All of our electronic components comply with ROHS, REACH\SVHC, halogen and other environmental protection directives as well as EU environmental protection requirements.
About Us
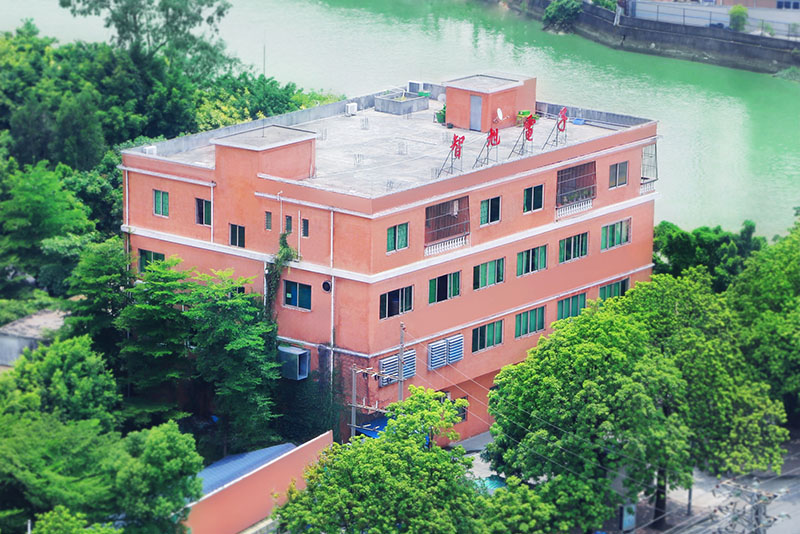

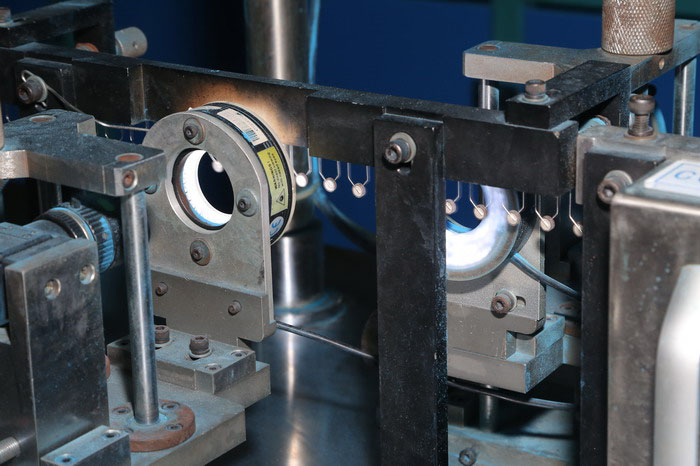
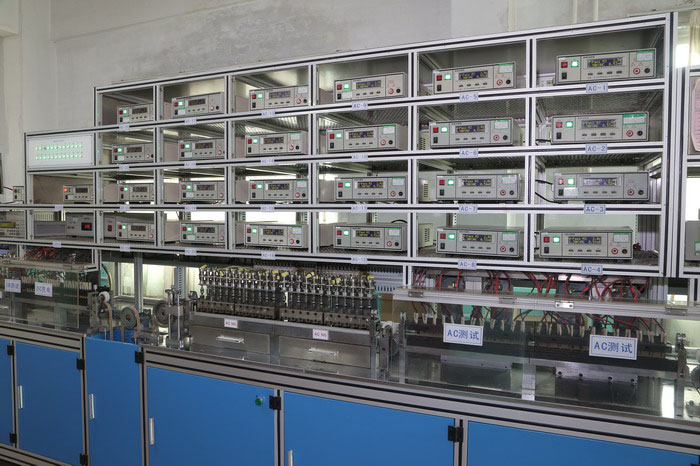
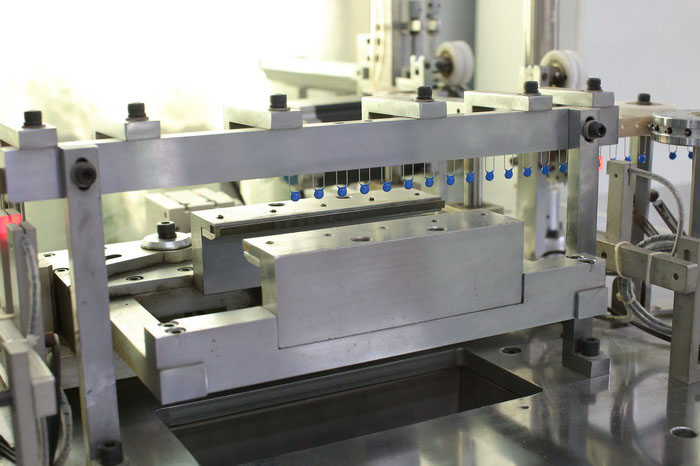
Advance Workshop
We not only possess a number of automated production machines and automated testing machines but also have our own laboratory to test the performance and reliability of our products.
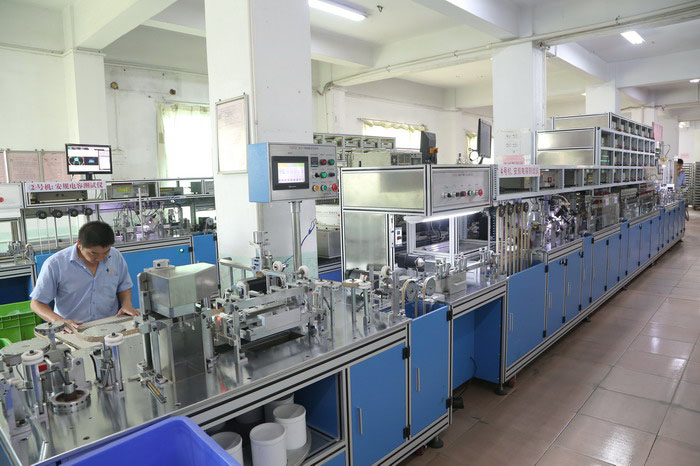








1. What is the difference between safety capacitors and ordinary capacitors?
The discharge of safety capacitors is different from that of ordinary capacitors. Ordinary capacitors will retain the charge for a long time after the external power supply is disconnected. Electric shock may occur if one touches an ordinary capacitor by hand, while there isn’t such problem with safety capacitors.
For safety and Electro Magnetic Compatibility (EMC considerations), it is generally recommended to add safety capacitors to the power inlet. At the input end of the AC power supply, it is generally necessary to add 3 safety capacitors to suppress EMI conduction interference. They are used in the power supply filter to filter the power supply.
2. What is a safety capacitor?
Safety capacitors are used in such occasions that after the capacitor fails: it will not cause electric shock and will not endanger personal safety. It includes X capacitors and Y capacitors. The x capacitor is the capacitor connected between the two lines of the power line (LN), and metal film capacitors are generally used; the Y capacitor is the capacitor connected between the two lines of the power line and the ground (LE, NE), and usually appears in pairs. Due to the limitation of leakage current, the Y capacitor value cannot be too large. Generally, the X capacitor is uF and the Y capacitor is nF. The X capacitor suppresses differential mode interference, and the Y capacitor suppresses common mode interference.
3. Why are some capacitors called safety capacitors?
The “safety” in safety capacitors does not refer to the capacitor material, but that the capacitor has passed the safety certification; in terms of material, the safety capacitors are mainly CBB capacitors and ceramic capacitors.
4. How many types of safety capacitors are there?
Safety capacitors are divided into X type and Y type.
X capacitors mostly use polyester film capacitors with relatively large ripple currents. This type of capacitor has a relatively large volume, but its allowable instantaneous charging and discharging current is also large, and its internal resistance is correspondingly small.
The capacitance of the Y capacitor must be limited, so as to achieve the purpose of controlling the leakage current flowing through it as well as the impact on the EMC performance of the system under the rated frequency and rated voltage. GJB151 stipulates that the capacitance of Y capacitor should not be greater than 0.1uF.