Can masks waste be used to create supercapacitor batteries? Researchers from the Russian National University of Science and Technology have developed a new technology that successfully utilizes discarded mask materials to produce supercapacitor batteries, with the battery casing made from pharmaceutical blister packaging. This research achievement addresses both the challenges of recycling used masks and the shortage of battery supplies. Additionally, the energy density of these new batteries is approaching that of regular lithium-ion batteries.
According to reports, the relevant research content was published in the February 2022 issue of the “Energy Storage” magazine. The content explains that supercapacitor batteries are a novel energy storage device that falls between traditional supercapacitors and rechargeable batteries. They possess the rapid charge and discharge characteristics of capacitors as well as the energy storage properties of batteries.
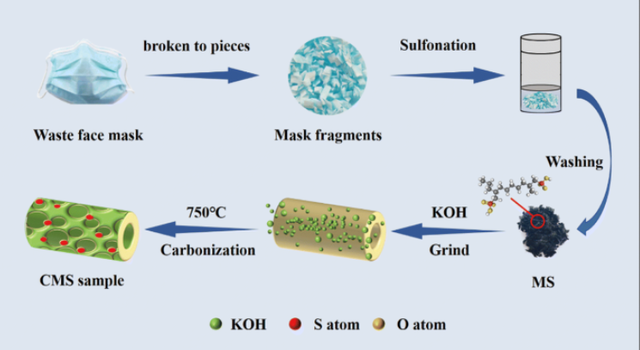
The materials primarily used in the fabrication of these new batteries include graphene, masks, and medical waste such as pharmaceutical packaging. The process involves initially disinfecting the mask waste using ultrasound, immersing it in a “ink” made of graphene, and then pressing and heating to create the battery electrodes. Subsequently, an insulating layer made from masks is placed between the two electrodes, followed by immersion in a special electrolyte. Finally, a protective casing is added to complete the production of the new type of battery.
Similar technologies have been used in the past to manufacture batteries, but the energy density was only around 10 Wh/kg. With the use of this new technology, the battery’s capacitance has been increased to 98 Wh/kg, which is quite close to mainstream lithium-ion batteries (with energy densities around 100 to 265 Wh/kg). Furthermore, the energy consumption during the battery manufacturing process has been reduced by a factor of 10, resulting in lower production costs and higher energy density. This innovation holds significant potential for development.
By incorporating auxiliary materials into the battery electrodes for further improvement, it’s possible to double the battery density, making it fully competitive with lithium-ion batteries. The current best-performing version of the supercapacitor battery retains around 82% of its capacitance after 1500 charge-discharge cycles. This battery is currently being used in household appliances like lamps and clocks, and there are plans to apply it in a broader range of applications, including electric vehicles and solar power plants in the future.
This article is provided by JYH HSU Electronics, a manufacturer that produces and sells different kinds electronic components such as capacitors and resistors.
Post time: Aug-24-2023