Supercapacitor modules often face the problem of voltage imbalance between cells. The so-called supercapacitor module is a module that contains several supercapacitors; because the parameters of the supercapacitor are difficult to be completely consistent, the voltage imbalance is prone to occur, and some supercapacitors may experience overvoltage, which seriously affects the output characteristics and life of the supercapacitor, and even leads to failure.
In the process of supercapacitor application, voltage balancing is necessary. The existing voltage balancing technology is mainly divided into two categories: passive balancing and active balancing.
Passive Balancing
Passive balancing is to use resistors and semiconductor switches or diodes to balance the voltage, and to play the role of overvoltage protection by consuming the excess energy of the high-voltage supercapacitor. Common ones include parallel resistor balancing, switch resistor balancing, and voltage regulator tube balancing.
Here we mainly talk about the simplest parallel resistor voltage balancing (dynamic characteristics are not very good):
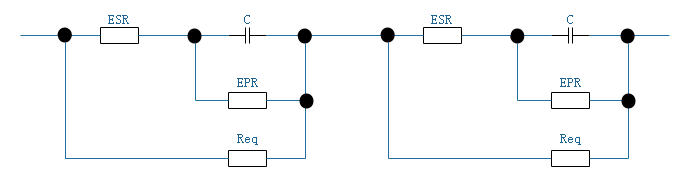
Req is a balancing resistor, which is directly connected in parallel with the supercapacitor cell. During the charging process of the module, the cell is also discharging through Req, and the cell with high voltage discharges quickly, thus playing the role of balancing protection. Here, according to the different charging methods (constant voltage charging and constant current charging, both of which can be used comprehensively in practical applications), there are also differences in the criteria for selecting Req.
Constant voltage charging
Assuming that the charging voltage is U, since the voltage of the supercapacitor module in the steady state is basically distributed according to the EPR (approximately open circuit after C is fully charged, and the ESR is very small), after adding Req, it can actually be understood as replacing EPR with Req, so Req must choose resistors with equal resistance and smaller than EPR, so that parallel connection can play a leading role (generally 0.01~0.1EPR). The voltage of the supercapacitor at steady state is ReqU/(nReq).
Constant current charging
Assuming that the charging current is I, each supercapacitor cell and Req form a separate loop. When the voltage of the capacitor cell rises, the current flowing through the capacitor cell drops, and the current flowing through Req increases. When the capacitor is fully charged, the current of the capacitor is 0, and the cell voltage of the capacitor is ReqI, that is, when the cell voltages of all series capacitors reach ReqI, the balancing is completed. Therefore, the value of the balancing resistor is Req=U(rated)/I.
Active Balancing
Active balancing is to transfer the energy of the higher voltage cell or the entire module to other cells until the voltage of all cells is balanced. Generally, the loss is relatively low, but the design will be more complicated. Common ones are DC/DC converter balancing, special super capacitor management chips, etc.
We’re JYH HSU(JEC) Electronics Ltd (or Dongguan Zhixu Electronic Co., Ltd.) that has over 30 years in the electronic components industry. Our factories are ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 certified. If you’re looking for electronic components, welcome to contact us.
Post time: Aug-17-2022